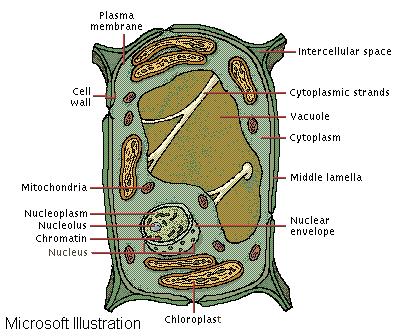

Plant cells, like animal cells, show a high degree of organization with membrane-bound internal structures. The nuclear envelope forms a barrier between the chromatin (genetic material) and cytoplasm of the cell. Convoluted mitochondria convert nutrients into energy the plant can use. Unlike animal cells, however, plant cells also contain chloroplasts, organelles capable of synthesizing energy from sunlight. Further differences include the cell wall, which contains cellulose and is quite rigid, and the fluid-filled vacuole, single and quite large in plants.
